A reducer motor, or gearmotor, typically employs various mechanical transmission systems, such as planetary gears, worm gears, and cylindrical gears, to achieve the desired output speed and torque. The gear ratio, or reduction ratio, of a gearmotor refers to the ratio between the rotational speeds of the transmission system and the motor’s output shaft rotor. This ratio can be calculated with the following formula, which assists in gear design and selection:
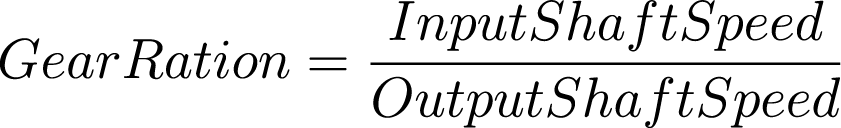
In this context, the output shaft speed refers to the rotational speed after it passes through the transmission system, while the input shaft speed is the motor’s original speed.



The gear ratio describes the change in speed output by the motor’s reduction device. Motors typically output at high speeds, but certain applications require lower speeds to meet specific needs. Here, the gearmotor comes into play, reducing the speed of the output shaft through the reduction device to provide the appropriate speed.
Selecting a gear ratio depends partly on the specific application requirements and partly on the gearmotor’s design and manufacturing costs. Generally, the gear ratio of a gearmotor is determined based on the needed speed and torque ratio. If a high torque and low speed output are required, a larger reduction ratio is needed. Conversely, for high speed and low torque output, a smaller reduction ratio may be suitable.
Choosing the right gear ratio also involves considering its effect on the gearmotor’s overall performance. As the gear ratio increases, so do the overall size and weight, which can impact efficiency. Therefore, when selecting a gear ratio, factors such as power requirements, size and weight restrictions, and efficiency should be taken into account.
The gear ratio of a gearmotor is generally determined by the configuration within the reduction device, such as the number of teeth on the gears or worm gears. For example, if the output shaft gear has 15 times more teeth than the input shaft gear, the reduction ratio is 15. Usually, the gear ratio is fixed, but in some cases, adjustable gearmotors allow for different gear ratios.
The importance of gear ratio selection varies across applications. Gearmotors are widely used in mechanical equipment like machine tools, conveyors, printing machines, and wind turbines, each with unique gear ratio requirements. Some applications need a higher gear ratio for greater torque, while others prefer a smaller ratio for higher speed.
Besides the gear ratio, other performance parameters—such as rated speed, rated power, and rated torque—are also essential in selecting a gearmotor. Only by carefully assessing the gear ratio alongside these parameters can the gearmotor function reliably in its application and meet user needs.
In summary, the gear ratio of a gearmotor defines the rotational speed relationship between the reduction device and the motor’s output shaft rotor. Selecting the right ratio is critical to achieving the desired output speed and torque, significantly affecting the performance of various mechanical systems.
For more insights into motors, contact us at Quadrant.
